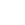
Discover the key differences between a car battery charger and jump starter. Learn when to choose each tool for emergencies or battery maintenance, how to safely use them, whether you can charge a jump starter with a battery charger, and which is better for trucks and everyday use. This guide explains battery charger vs jump starter, helps you choose the most practical option for everyday use or emergency truck starting solution.
What’s the Difference Between a Battery Charger and a Jump Starter?
A car battery charger and a jump starter are both essential automotive tools, but they serve very different purposes and excel in distinct scenarios. Understanding the difference between battery charger and jump starter is critical when choosing the right solution for your vehicle’s needs.
Table: Comparison in battery charger and jump starter
|
Feature
|
Battery Charger
|
Jump Starter
|
|
Purpose
|
Slow, controlled charging and battery maintenance
|
Instant power surge for emergency engine start
|
|
Power Source
|
Plugs into AC outlet
|
Internal rechargeable battery
|
|
Function
|
Recharges and maintains battery health over time
|
Provides a high burst of power to start engine
|
|
Best Use Scenarios
|
Long-term battery maintenance, battery recovery
|
Emergency restart in dead battery situations
|
|
Operation Time
|
Several hours to overnight
|
Instant, within seconds
|
|
Portability
|
Bulkier, requires power outlet
|
Compact, portable, no external power needed
|
|
Safety Features
|
Overcharge protection, automatic shutoff
|
Reverse polarity protection, short burst use
|
|
Typical Users
|
Garage use, seasonal vehicles, battery recovery
|
Roadside emergency kits, drivers in remote areas
|
|
Additional Features
|
Smart charging technology
|
Often includes USB ports, LED flashlight, air compressor
|
|
Battery Impact
|
Extends battery lifespan
|
Does not recharge battery; alternator needed after jump start
|
Jump Starter vs Battery Charger: Which to Use and When
Functionality:
A battery charger is engineered for gradual, controlled charging and long-term battery maintenance. It connects to your vehicle’s battery and uses an external AC power source, slowly replenishing charge over several hours. Smart chargers can optimize charging rates, prevent overcharge, and enhance overall battery life.
In contrast, a jump starter delivers a high-intensity surge of power—instantly cranking your engine for a quick start while your battery is dead. This device has its own internal battery, making it fully portable and not dependent on a power outlet or another vehicle.
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a battery charger is to recharge a depleted battery gradually, to bring it back to a full state of charge or maintain it in a ready condition during storage or long periods of inactivity. It’s not intended for engine starting. On the other hand, a jump starter is purpose-built for emergencies: starting a vehicle when the battery is critically low or completely dead. It acts like a temporary surge source, supplying enough power to spin the starter motor and ignite the engine.
Use cases:
1.Battery charger: Routine battery health maintenance, recovering deeply discharged batteries, long-term storage, overnight charging.
2.Jump starter: Sudden battery failure, cold weather, remote locations, urgent restarts without access to power or assistance.
Operation Details:
To operate a battery charger, you connect it to the vehicle battery (still connected or removed), plug the charger into an AC outlet, and let the device monitor and recharge over time—usually several hours or overnight.
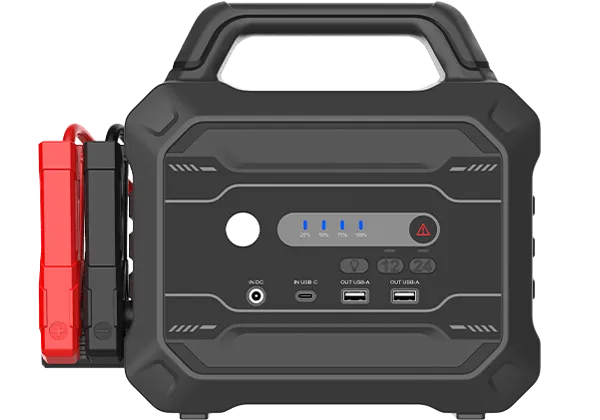
For a jump starter, you only need to attach its clamps to your battery’s terminals and power it on; within seconds, it delivers a large current to start your engine. Many jump starters now include built-in features for added convenience, such as USB charging, integrated flashlights, or air compressors for roadside emergencies.
Amps Guide: Peak Current Essentials
Before attempting to perform a hitch start for your truck, make sure that all power load devices on your vehicle are turned off.
1. Press the power button to start. All LEDs will flash indicating that all LEDs are working properly.
2. If the battery clips are connected correctly, press boost and the green LED will illuminate. If the battery clips are connected backwards, the red LED will illuminate.
3. When the green start LED is lit, it indicates that the starter unit is ready to start the vehicle.
4. Start the vehicle. Some vehicles may take up to 30 seconds to start with Boost connected.If the vehicle does not start immediately, wait 20 or 30 seconds and then start the vehicle again.Do not make more than a few consecutive starting attempts in a 15 minute period. After starting the vehicle, disconnect the battery clamps and remove the Boost.
Before comparing models, it’s important to understand why peak current (peak amps) matters in real jump-starting scenarios. Unlike a charger that restores power slowly, a jump starter relies entirely on its ability to deliver a short, high-amp burst. We won’t repeat the full comparison here—what matters in this section is how much peak current your vehicle actually needs.
Peak amps determine a jump starter’s capability to turn over different engine sizes. Higher peak current doesn’t always mean better performance, but it does expand compatibility across more demanding applications—especially diesel trucks, heavy-duty engines, commercial vehicles, and equipment with large displacement or high compression.
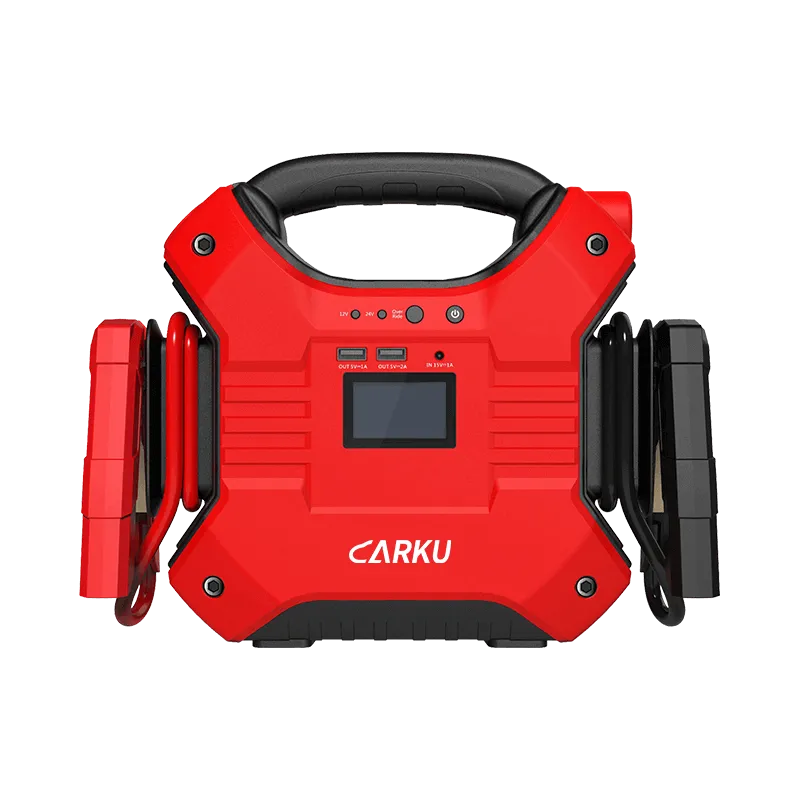
For example, small gasoline cars may need only 500–1000A, while jump starters for trucks typically require 2000A–4000A to confidently start an engine in cold weather or low-battery conditions. This is why high-amp models are preferred by long-haul drivers, fleet operators, and anyone who needs reliable emergency starts rather than waiting for a battery to recharge.The JS393B jump starter delivers 3,000 peak amps, making it suitable for heavy-duty trucks, pickup trucks, light duty trucks, and tractors.
How To Jump-start a Heavy Duty Truck?
Before attempting to perform a hitch start for your truck, make sure that all power load devices on your vehicle are turned off.
1. Press the power button to start. All LED will flash indicating that all LED are working properly.
2. If the battery clips are connected correctly, press boost and the green LED will illuminate. If the battery clips are connected backwards, the red LED will illuminate.
3. When the green start LED is lit, it indicates that the starter unit is ready to start the vehicle.
4. Start the vehicle. Some vehicles may take up to 30 seconds to start with Boost connected.If the vehicle does not start immediately, wait 20 or 30 seconds and then start the vehicle again.Do not make more than a few consecutive starting attempts in a 15 minute period. After starting the vehicle, disconnect the battery clamps and remove the Boost.
For trucks with weak batteries, a jump starter is far more practical than relying on a slow battery charger.
What Is The Best Jump Starter For a Truck?
Choosing the best jump starter for a truck requires more capability than what is needed for standard passenger vehicles. Trucks—especially diesel, commercial, and heavy-duty models—demand higher cranking power, compatibility with 12V and 24V systems, reliable performance in cold climates, and enough stored energy for repeated starts without recharging.
-
Battery Capacity: 352,000mAh (1133.44Wh)
-
Charging Time: About 2 hours (via USB-C and DC 29V/5A inputs)
-
Peak Current: 8,000A, providing enough power to start large engines quickly and reliably
-
Voltage Compatibility: Supports both 12V and 24V systems, suitable for various truck types including heavy-duty and commercial vehicles
-
Weight and Size: Robust build at 13.5kg and dimensions of 340.5×222.5×263mm, designed for industrial and fleet use
-
Operating Temp: Works effectively in extreme conditions from -40℃ to 60℃
Why JS396 Is Ideal for Trucks?
The JS-396 exemplifies what defines a top-tier jump starter for a truck. With an impressive 8000A peak current, it provides the burst power required to start heavy-duty diesel engines and 24V commercial vehicles with confidence. Its massive 352000mAh (1133.44Wh) battery capacity allows multiple starts on a single charge—ideal for roadside service operators, fleet managers, and professional drivers.
Designed to perform in extreme working environments from -40℃ to 60℃, it ensures reliable cranking even in freezing winter conditions where batteries lose efficiency. Supporting both 12V and 24V systems, fast charging in about 2 hours, and equipped with functional USB outputs for auxiliary devices, it offers a practical and versatile solution for professional-grade use.
For truck owners, heavy-duty equipment operators, and long-distance drivers, a model with this level of current delivery, cold-weather reliability, and dual-voltage compatibility represents the most dependable and practical choice when selecting the best jump starter for a truck.
Jump Starter Battery Types Explained
Choosing the right battery type for a jump starter is essential not only for performance but also for maintenance and lifespan. Here, we explain the three main types of jump starter batteries—Lithium-ion, LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate), and Lead Acid, and their impact on battery maintenance and cycle life.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that are widely used in electronic devices such as laptops and cell phones. They are also used in many emergency starting power sources and in electric vehicles.
One of the great things about lithium-ion batteries is their high energy density! This means they can pack a lot of energy into a small space, making them super efficient. They also have a long lifespan, usually at least five years, and a cycle life of up to 3,000 cycles. In addition, they are relatively low maintenance. In the long run, this is a desirable option for many buyers jump starting a car and charge electronics.
LiFePO4 Batteries
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are often abbreviated as LFP or LiFePO4. Currently, many new energy companies are using LFP batteries in their portable power stations and solar power kits.
There are significant differences between LFP batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Conventional lithium-ion batteries typically use cobalt, while lithium iron phosphate batteries use a composite of iron phosphate and graphite. The cobalt contained in Li-ion batteries in electric vehicles is toxic, making LiFePO4 batteries a more environmentally friendly alternative.
LFP batteries are typically more efficient in terms of energy storage, have a longer lifespan, and can operate over a wider temperature range without performance degradation. LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries are the best choice for off-grid living (no electricity supply). They are more efficient, charge faster, last longer, and have a lower environmental impact.
Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries represent the traditional choice in jump starters. While they are relatively inexpensive and capable of delivering high power output, they are heavier and bulkier due to their lower energy density. Maintenance requirements are higher — regular checks and refilling of electrolyte levels are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Lead acid batteries also generally have shorter cycle lives and degrade faster over time, requiring more frequent replacement compared to lithium-based options.
Battery Maintenance Summary
Lithium-ion and LiFePO4 batteries demand minimal maintenance, mostly involving keeping the battery charged and avoiding deep discharge. Lead acid batteries require more hands-on upkeep such as periodic electrolyte refills and protection against over-discharge to prolong life cycles.
Which Is Better? Battery Charger vs Jump Starter for Trucks: Full Comparison
When comparing truck battery chargers and jump starters, jump starters are indeed the more practical emergency tool. The 2025 comparison guide for battery chargers versus jump starters is as follows:
Emergency readiness: Jump starters provide immediate power to start a dead battery, critical in urgent situations where waiting is not an option. Whereas the battery charger requires hours to recharge the battery.
Portability: Compact and self-contained, jump starters can be kept in your vehicle for quick access, ideal for roadside emergencies. Whereas the battery charger typically stays in garage or workshop.
Suitability for heavy-duty vehicles: Jump starters with higher peak amps (e.g., 3000A JS393B model) cater to trucks, pickups, tractors, providing the burst power needed for large engines. Whereas the battery charger
Versatility in remote or cold conditions: Jump starters work without the need for external power, essential for remote travels, cold weather, and locations without power outlets.
Long-term use for truckers: Heavy-duty lead-acid jump starters offer durability for frequent jumps in extreme environments; lithium jump starters provide safety, reliability, and convenience for most personal and emergency use cases.
Additional features: Modern jump starters often include USB ports, integrated flashlights, and air compressors to enhance roadside utility.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Can I charge a jump starter with a battery charger?
Yes, you can charge a jump starter with a compatible battery charger, provided it supports the jump starter’s battery type and voltage. Most lithium jump starters require the use of a low-amp smart charger to prevent overcharging and extend battery life. Using a non-smart conventional car battery charger may damage the device or shorten battery lifespan. It is recommended to use the manufacturer-recommended smart charger to ensure safe and efficient maintenance.
2.Can you jump a truck with a battery charger?
The JS393B jump starter has a powerful built-in battery pack. Jump-starting your truck with the smart jump cable protects against short circuits and operational errors.
3.Should I buy a battery charger or a jump starter?
As an occasional user, the battery charger is used as a home scenario. As a regular user, the portable starter is placed in the trunk of the car for emergency use. There is no need to worry about leaving it for months without power.
4.How long does it take to jumpstart a car with a portable charger?
A 12-volt car battery with a capacity of about 10,000 mAh (10 amps) will take about 8 hours at 5 volts/2 amps input.
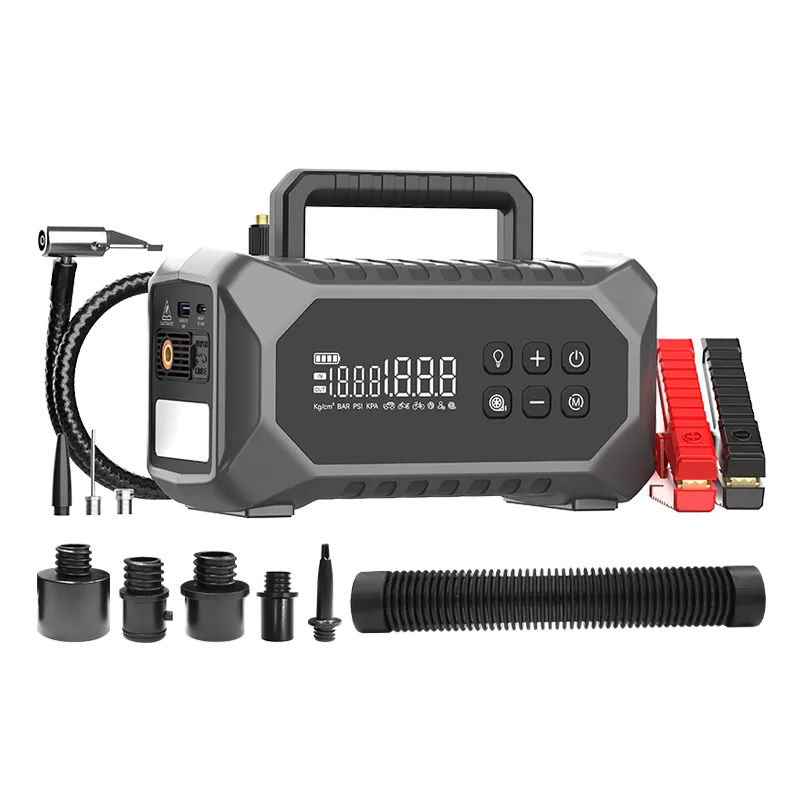
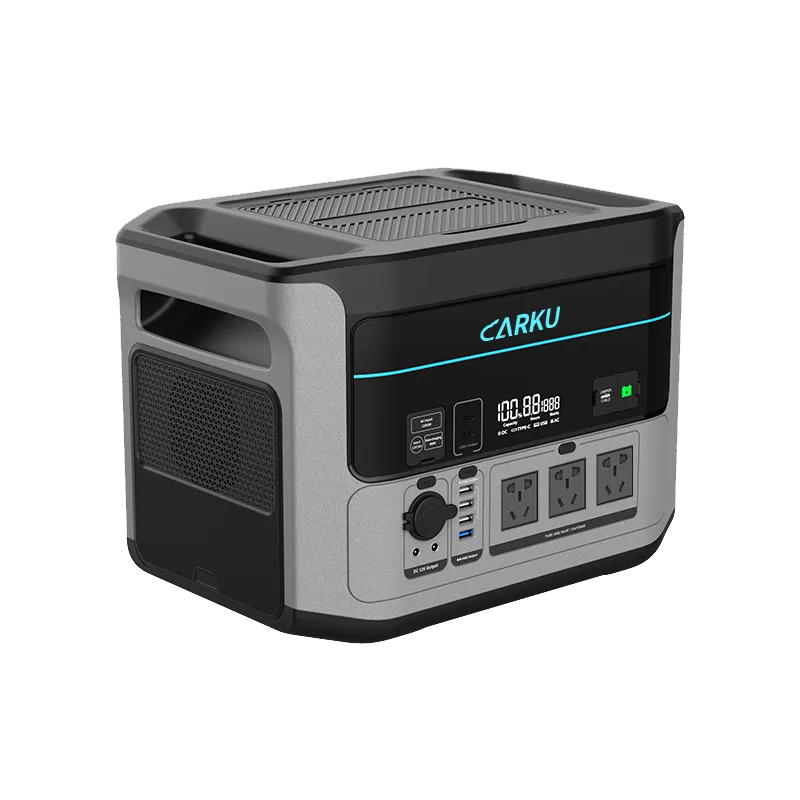
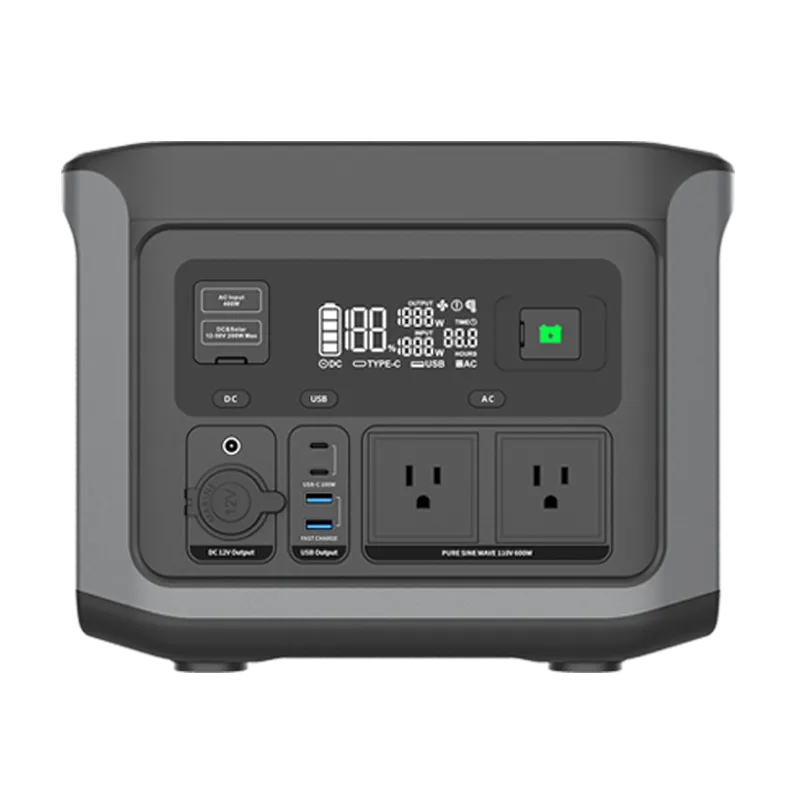
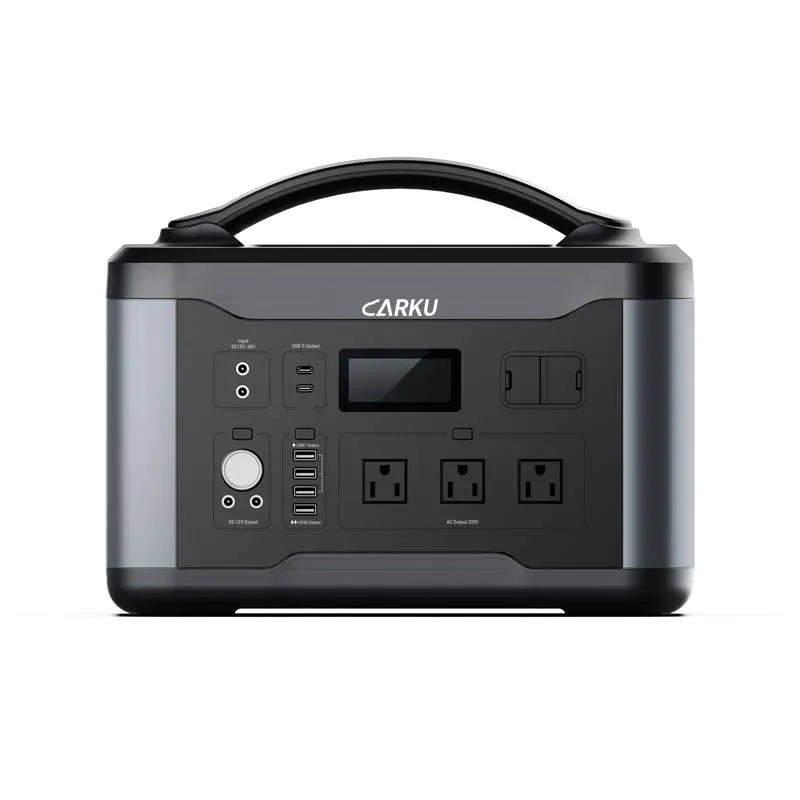































 Jump Starter ODM/OEM Solutions
Jump Starter ODM/OEM Solutions Portable Power Station ODM/OEM Solutions
Portable Power Station ODM/OEM Solutions Starting Battery ODM/OEM Solutions
Starting Battery ODM/OEM Solutions ABOUT CARKU
ABOUT CARKU STRENGTH FACTORY
STRENGTH FACTORY THE DEVELOPMENT HISTORY OF CARKU
THE DEVELOPMENT HISTORY OF CARKU CORE COMPETITIVENESS
CORE COMPETITIVENESS COMPANY CULTURE
COMPANY CULTURE QUALIFICATION
QUALIFICATION
 CARKU News
CARKU News CARKU Exhibitions
CARKU Exhibitions CARKU Battery Applications
CARKU Battery Applications